How to understand the different technical information of a wheel
BOLT PATTERN: The bolt pattern represents an imaginary circle going through the centre of the wheel lugs. The most common bolt patterns in the industry are 4, 5, 6 or 8-lug holes. For example, a 5 x 114.3 bolt pattern represents a 5-lug pattern on a 114.3 mm diameter circle.
CENTRE BORE: The centre bore is the large middle hole machined in the wheel to properly seat the wheels on the vehicle hub. It is important that the wheel’s centre bore matches the vehicle’s hub size. Most aftermarket wheels are machined with a larger bore to fit more vehicles and they use hub-centric rings to adapt to the car they’re installed on. These rings have an outside diameter with the wheel centre bore size and an inner diameter matching the vehicle hub size, making sure it fits perfectly no matter on what vehicle you’re installing the wheels. On the other hand, many replica wheels are machined with the exact diameter to fit on the car they’re intended for. For steel rims, a lot of them are not hub centric but lug centric, meaning they are centred by the lugs. It is important to always install these with the vehicle on safety stands with the wheels off the ground. The wheel will centre when tightening the nuts down, and not having the weight of the vehicle resting on the wheel will prevent it from being pushed off centre.
LUG CENTRIC: Most aftermarket wheels are made with a larger hub to ensure that they will fit on a wide range of vehicles. This means that when the wheel is installed, there will most likely be a space between the axle and the hub instead of a firm contact. The wheel is therefore lug centric, as the wheel is centred by the lugs rather than by the hub. In the case of steel rims, we cannot put centring rings! There is no danger putting these rims on. Most vehicles on the road will have these lug-centric rims since they are more popular with garages. They only have to stock a small amount compared to a hub-centric wheel.
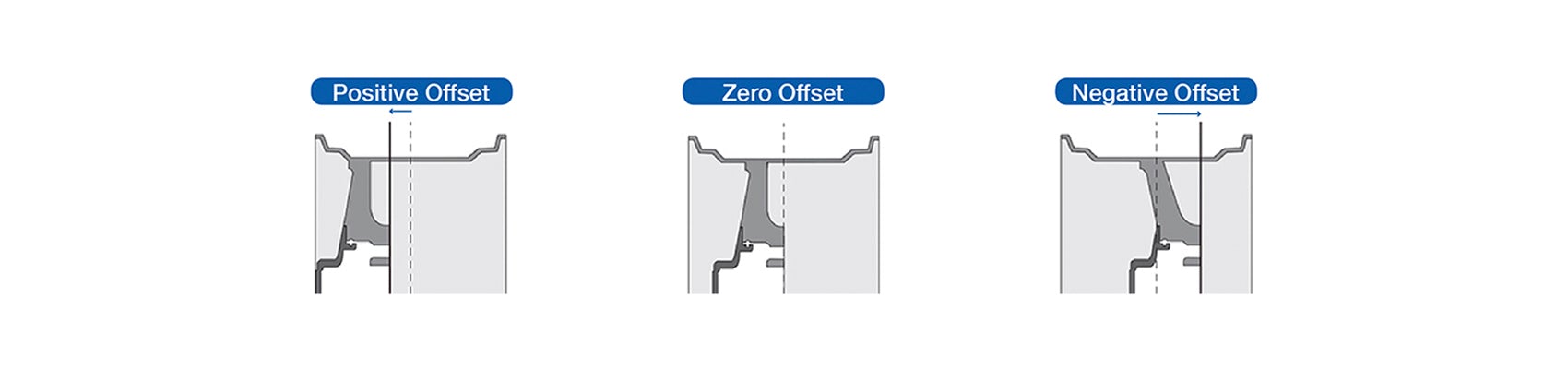
OFFSET: The offset is the measure of the distance between the centre of the wheel to the hub mounting point on the wheel.
There are 3 categories of offset:
A. ZERO OFFSET: This is when the hub mounting point on the wheel is aligned with the middle of the wheel. This kind of offset is mostly used for older rear wheel drive cars or for pickup trucks with large fenders.